Jellyfish and the Audit Logging Service
The Audit Logging Service provides complete and tamper-proof visibility into user and system activity across all endpoints. It enables administrators to track, analyze, and respond to events within their tenancy by capturing a detailed record of every operational interaction. The service maintains strict data isolation, ensuring that only authorized users within a tenancy can access and analyze their respective audit trails. The Jellyfish RBAC ensures granular minimally scoped access to audit components.
Whether responding to incidents, validating compliance, or tracking down the root cause of an operational issue, the audit logging service plays a central role in maintaining trust, transparency, accountability, and security.
Comprehensive and High-Fidelity Logging
Each audit event captures a set of metadata fields designed to offer complete insight into user behavior and system function.
Logged attributes include:
- user identifiers
- source IP addresses
- endpoint names
- tenancy IDs
- event types (e.g., read, write, modify, delete)
- operation status codes
- supplementary event details
- precise timestamps.
This high level of detail provides the foundation for forensic investigation, operational troubleshooting, behavioral analytics, and compliance verification. Every action that modifies or interacts with a critical service component is logged, timestamped, and preserved in a secure and immutable format.
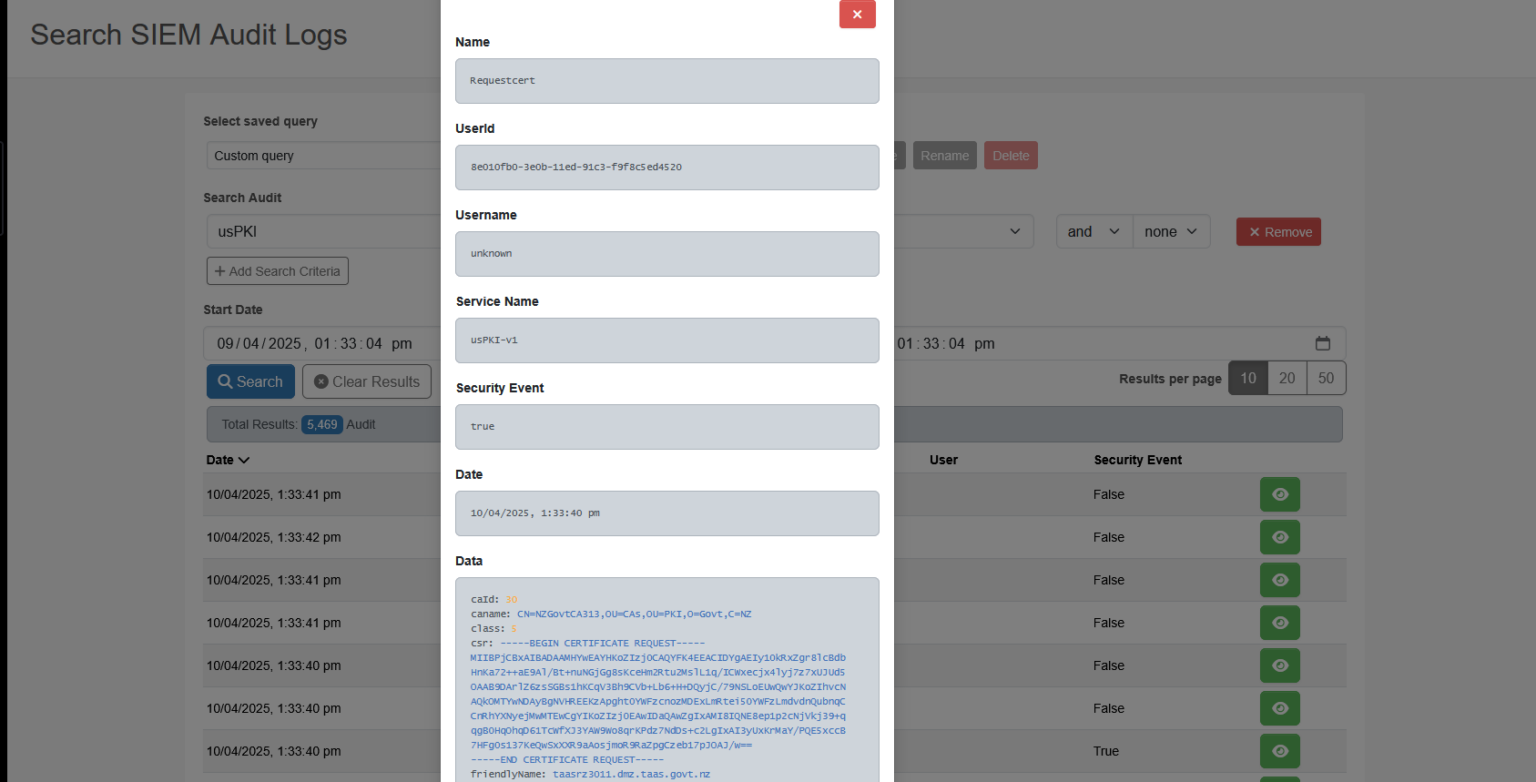
Figure 1: Audit logs event details
Enforced Logging and Fail-Safe Mechanisms
The audit logging service supports multiple access modalities to suit a wide range of operational and analytical workflows. Users can interact with the logs through a graphical user interface (GUI), enabling intuitive exploration and filtering of audit events in real time. For automation or large-scale analysis, the service provides a robust API that allows users to query logs programmatically and integrate the results into internal tooling or platforms.
Access Channels and Integration Flexibility
The audit logging service supports multiple access modalities to suit a wide range of operational and analytical workflows. Users can interact with the logs through a graphical user interface (GUI), enabling intuitive exploration and filtering of audit events in real time. For automation or large-scale analysis, the service provides a robust API that allows users to query logs programmatically and integrate the results into internal tooling or platforms.
Rest API
The Audit Logging Service offers secure access to audit data through a REST API, enabling organizations to automate log retrieval and integrate audit visibility into their internal systems. Using the API, users can perform filtered queries based on timeframes, user IDs, event types, and more, with responses returned in a structured JSON format.
This programmatic access allows teams to automate tasks such as alerting, reporting, and log ingestion into dashboards or SIEM solutions. It reduces manual overhead and frees security and operations teams to focus on investigation and response activities rather than routine data collection.
Inquire about the Rest API documentation for more information.
Advanced Search and Event Filtering Capabilities
The search functionality within the audit logging service is both powerful and granular. Users can define custom timeframes and apply multiple conditionals across various fields, such as service name, message body content, user ID, endpoint name, and event classification. Security-specific events can be isolated for targeted analysis, and unique identifiers such as event IDs or custom correlation tags can be used to trace chains of actions across systems.
These advanced filtering capabilities make the service a highly effective tool for conducting investigations, supporting compliance audits, or analyzing patterns that may indicate policy violations, insider threats, or unauthorized changes.
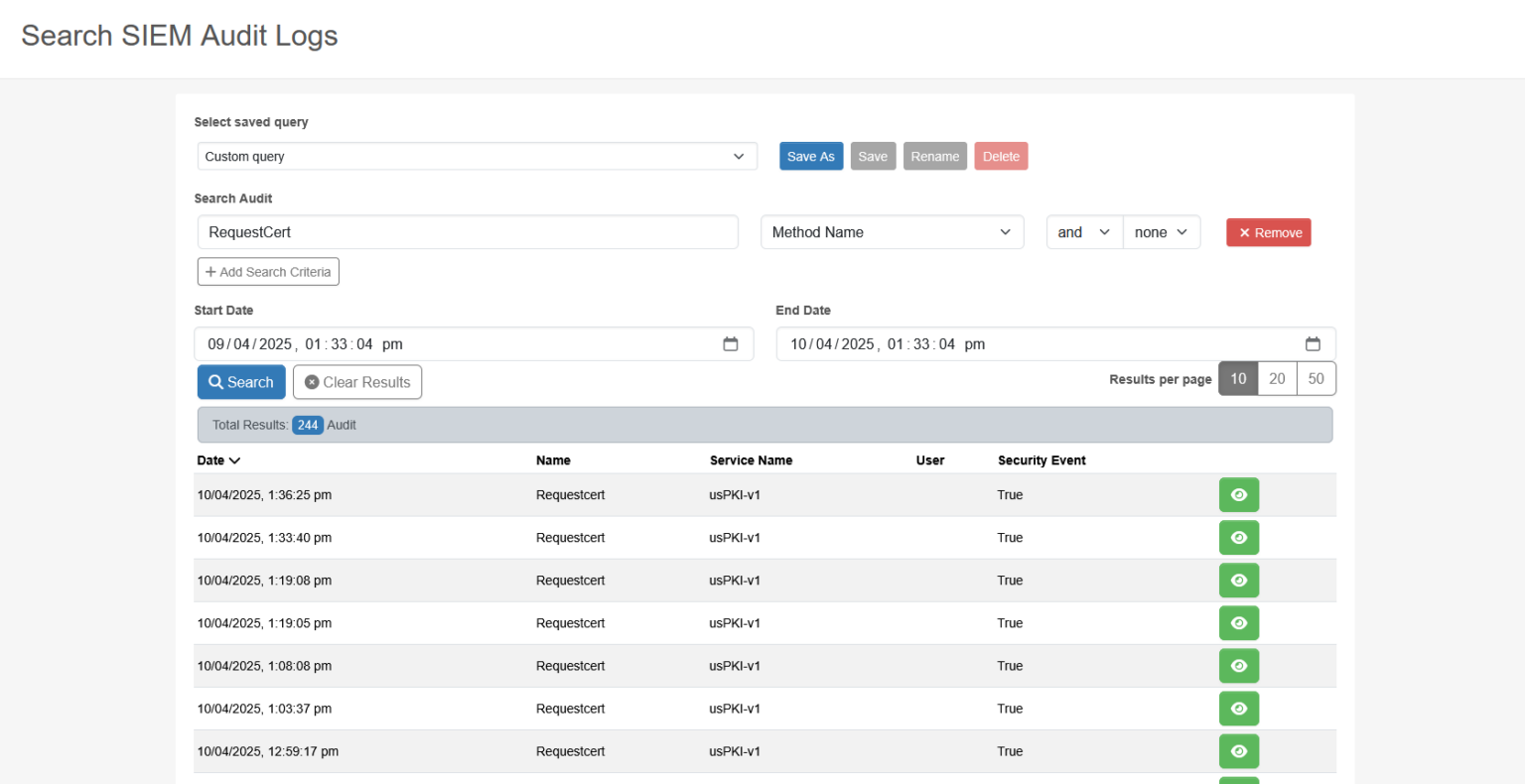
Figure 2: Audit logs Search function
Usefulness in Incident Response and Forensics
Security teams can identify unauthorized access attempts, track configuration changes, verify the presence of malicious inputs, and validate whether data was accessed, exfiltrated, or modified. Without a reliable logging mechanism, such investigations would rely on assumptions, estimations, or incomplete snapshots of system state.
Audit logging transforms these scenarios into verifiable, evidence-driven analyses.
